Plasticity model for superelastic materials | ||||||||||
|
| |||||||||
ProductsAbaqus/StandardAbaqus/ExplicitAbaqus/CAE
Material behavior
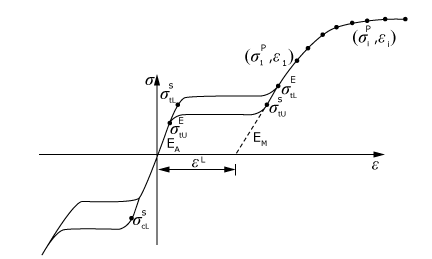
The plasticity model for superelastic materials is based on the uniaxial stress-strain response, as shown in Figure 1. Such materials (e.g., Nitinol) are in the austenite phase under no loading conditions. Austenite is assumed to follow isotropic linear elasticity. On loading the material, the austenite phase starts transforming into martensite beyond a certain stress. Martensite is assumed to follow an elastoplastic response, with elasticity characterized by the linear elastic model and the plastic behavior represented by the Drucker-Prager model. Martensite exhibits plastic behavior after full transformation.
In this model the total strain increment, is assumed to be the sum of the elastic strain increment, , the increment in transformation strain, , and the increment in plastic strain, :
The increment in plastic strain is calculated using a nonassociated flow rule:
where is the plastic flow potential, is equal to the Mises equivalent stress,
The yield surface, , is assumed to follow the Drucker-Prager formulation with hardening driven by the equivalent plastic strain, :
where is the pressure and is the friction angle. The initial yield stress is the stress at which the transformation of austenite into martensite ends,
Input File Usage
Use the following option to define the yield stress as a function of total strain.
SUPERELASTIC HARDENING
Abaqus/CAE Usage
Use the following option to define the yield stress as a function of total strain.
Property module: material editor: :
Superelastic hardening modifications
It is observed that the transformation stress levels decrease with an increase in the plastic strain. There are two ways to specify this variation in the transformation plateau with plastic strain in Abaqus. You can either specify the data describing the change in transformation stress levels as a function of the plastic strain or you can use a user subroutine to specify this dependency. USUPERELASHARDMOD should be used in Abaqus/Standard, and VUSUPERELASHARDMOD should be used in Abaqus/Explicit.
Input File Usage
Use the following option to specify the data to define the dependence of the transformation stress levels on plastic strain:
SUPERELASTIC HARDENING MODIFICATIONS
Use the following option to define the dependence of the transformation stress levels on plastic strain in a user subroutine:
SUPERELASTIC HARDENING MODIFICATIONS, USER
Abaqus/CAE Usage
Use the following option to specify the data to define the dependence of the transformation stress levels on plastic strain:
Property module: material editor: :
Use the following option to define the dependence of the transformation stress levels on plastic strain in a user subroutine:
Property module: material editor: : : toggle on User
![]()
Elements
The plasticity model for superelastic materials can be used with any stress/displacement element in Abaqus.