Define Symmetry Conditions in Tosca ANSA® environment
Choose DV_CONSTRAINTS and select . In order to define a symmetry condition, enter following settings in the SYMMETRY_CONTROL dialog:
- Reflection symmetry (TYPE = PLANE_SYM): the symmetry
plane is identified by a point (ORIGIN_1..ORIGIN_3)
and the normal direction (DIRECTION_1..DIRECTION_3).
- Rotation symmetry (TYPE = ROTATION_SYM): the rotation
axis is defined by a point (ORIGIN_1..ORIGIN_3) and
the direction (DIRECTION_1..DIRECTION_3); the field
ANGLE is the rotation angle.
- Cyclic symmetry (TYPE = CYCLIC_SYM): the translation
direction is defined by a point (ORIGIN_1..ORIGIN_3)
and the direction (DIRECTION_1..DIRECTION_3); the field
TRANSLATION is the translation distance.
Note:
Although the origin has no influence, it should be specified because
SIMULIA Tosca Structure
requires that the direction is an axis of a coordinate system. In this
case, this coordinate system is created automatically by Tosca ANSA® environment.
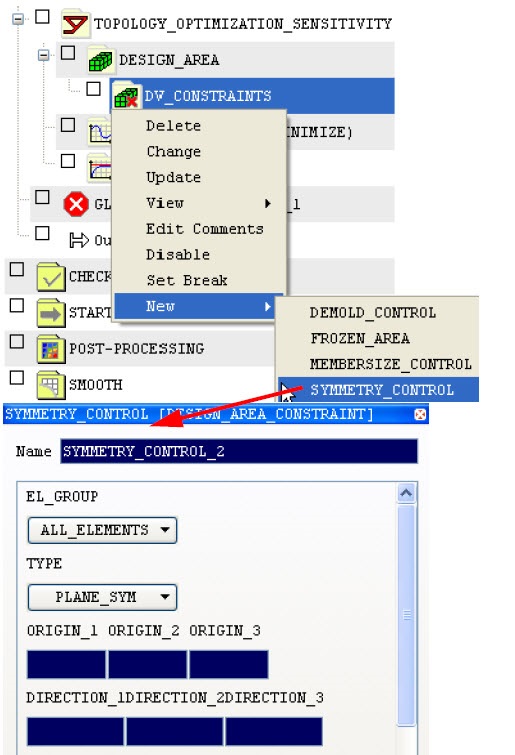
In each case, EL_GROUP is the element group that the symmetry
condition applies to.

Define Symmetry Conditions in Tosca Structure.gui
Choose . In the LINK_TOPO menu, define the type of symmetry,
the coordinate system and, if necessary, the rotation angle (in case
of rotation symmetry) or the translation distance (in case of cyclic
symmetry). The symmetry definition can also be extended to frozen areas
by selecting the corresponding checkbox. The frozen elements of one area are also considered as frozen for
the linked areas if Frozen checkbox is checked. Select . In the DVCON_TOPO dialog, apply the defined LINK_TOPO to an element group as shown in the following figure:
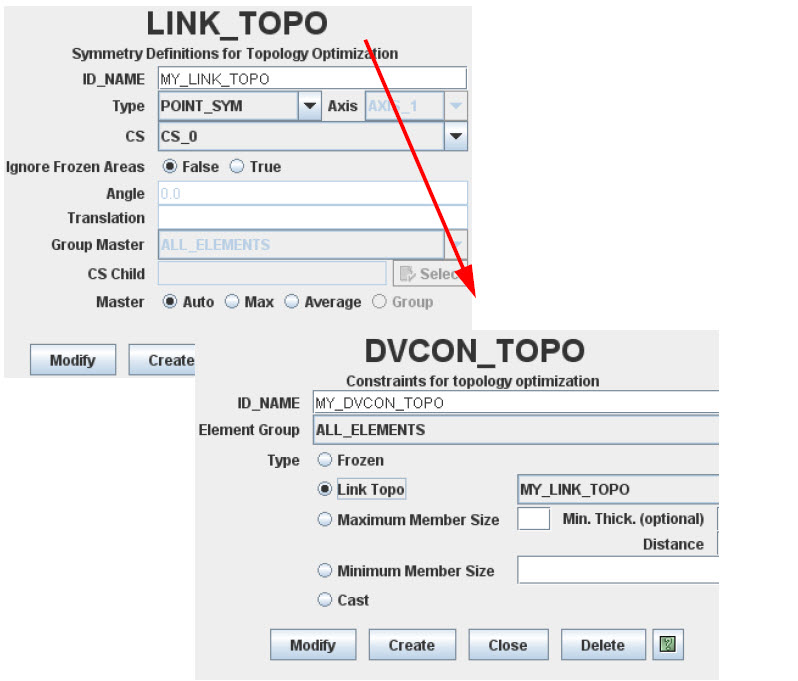
The corresponding parameter file looks like:
LINK_TOPO
ID_NAME = <Name of LINK_TOPO object>
CS = <Name of the reference coordinate system>
TYPE = <Type of symmetry>, <axis>
TRANSLATION = <Translation for cyclic symmetry>
ANGLE = <Segment angle for rotation symmetry>
END_
DVCON_TOPO
ID_NAME = <Name of DVCON_TOPO object>
EL_GROUP = <Element group to be restricted>
CHECK_TYPE = LINK_TOPO
CHECK_LINK = <Name of LINK_TOPO definition>
END_
More than one symmetry condition can be defined for an element group.
Geometrically, different combinations have to be feasible.
|
![]()