Constructor contents | ||
| ||
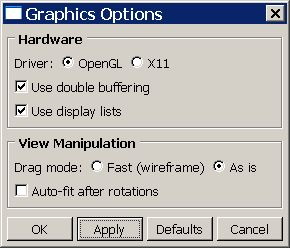
To keep the GUI up-to-date with the application state and vice versa, you use keywords as targets of widgets. Keywords are defined as members of a form, and the form is passed to the dialog box as a dialog box constructor argument. For more information, see AFXKeywords. The following script shows how you can use keywords to construct a dialog box. Figure 1 shows the Graphics Options dialog box generated by the example script.
Figure 1. Graphics Options data dialog box.

class GraphicsOptionsDB(AFXDataDialog):
#~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
def __init__(self, form):
AFXDataDialog.__init__(self, form, 'Graphics Options',
self.OK|self.APPLY|self.DEFAULTS|self.CANCEL)
# Hardware frame
#
gb = FXGroupBox(self, 'Hardware',
FRAME_GROOVE|LAYOUT_FILL_X)
hardwareFrame = FXHorizontalFrame(gb,
0, 0,0,0,0, 0,0,0,0)
FXLabel(hardwareFrame, 'Driver:')
FXRadioButton(hardwareFrame, 'OpenGL',
form.graphicsDriverKw, OPEN_GL.getId())
FXRadioButton(hardwareFrame, 'X11',
form.graphicsDriverKw, X11.getId())
FXCheckButton(gb, 'Use double buffering',
form.doubleBufferingKw)
displayListBtn = FXCheckButton(gb, 'Use display lists',
form.displayListsKw)
# View Manipulation frame
#
gb = FXGroupBox(self, 'View Manipulation',
FRAME_GROOVE|LAYOUT_FILL_X)
hf = FXHorizontalFrame(gb, 0, 0,0,0,0, 0,0,0,0)
FXLabel(hf, 'Drag mode:')
FXRadioButton(hf, 'Fast (wireframe)', form.dragModeKw,
FAST.getId())
FXRadioButton(hf, 'As is', form.dragModeKw,
AS_IS.getId())
FXCheckButton(gb, 'Auto-fit after rotations',
form.autoFitKw)