Context:
You create an extruded cut into a three-dimensional part by sketching the two-dimensional cross-section of the cut on a selected face and defining the distance through which Abaqus/CAE extrudes the cut. You can select one of the following methods to define the distance through which the cut is extruded:
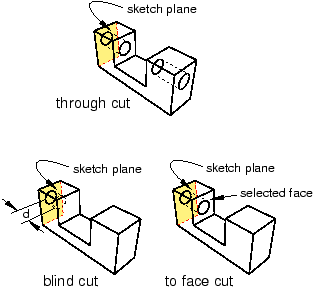
Blind extends the cut from the sketch plane in a selected direction but only to a specified depth.
Up to Face extends the cut from the sketch plane to a selected face.
Through All extends the cut from the sketch plane in a selected direction through the geometry.
The three methods are illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Three methods for creating an extruded cut.
You create an extruded cut in a two-dimensional or axisymmetric planar part by sketching the two-dimensional cross-section of the cut directly on the plane of the part. The cut always passes completely through the part.
When creating an extruded cut in a three-dimensional part, you can select a center point and specify a pitch that Abaqus/CAE uses to twist the cross-section as it is extruded. Alternatively, Abaqus/CAE can expand or contract the cross-section along a specified draft angle as the cross-section is extruded. For more information, see Including twist in an extrusion, and Including draft in an extrusion.
From the main menu bar, select .
Abaqus/CAE displays prompts in the prompt area to guide you through the procedure.
If desired, specify the method you want to use to select an origin for your sketch of the extruded cut feature. Select one of the following options from the Sketch Origin field in the prompt area:
-
Select Auto-Calculate to place the sketch origin automatically.
-
Select Specify to define a custom sketch origin.
-
Select Session Default to use the custom origin you specified earlier in the session.
If the current viewport contains a two-dimensional or axisymmetric planar part, Abaqus/CAE enters the Sketcher and you sketch the closed profile of the extruded cut on the plane of the part.
If the current viewport contains a three-dimensional part, you must do the following:
- Select the planar face from which the cut will be extruded. If no suitable face exists, you can select a datum plane or an orphan element face.
The selected face is highlighted in the viewport.
- If you selected Specify as the Sketch Origin method, specify the origin location by clicking a point in the viewport or by entering the three-dimensional coordinates of the origin in the prompt area. You can also set this custom origin as the default origin for all sketches in your session by toggling on Set as session default.
- Select an edge and the orientation of the edge on the Sketcher grid. The edge must not be perpendicular to the selected face. By default, the selected edge will appear vertical and on the right side of the Sketcher grid. To choose a different orientation for the edge, click the arrow on the right side of the dialog box and choose an orientation from the list that appears.
Abaqus/CAE highlights the selected edge, enters the Sketcher, and rotates the part until the selected face aligns with the plane of the Sketcher grid and the selected edge aligns with the grid in the desired orientation.
If you are unsure of the part's orientation relative to the Sketcher grid, use the view manipulation tools from the View Manipulation toolbar to view its position. Use the reset view tool  to return to the original view.
to return to the original view.
- Use the Sketcher to sketch the closed two-dimensional profile of the extruded cut.
In the prompt area, click Done to indicate you have finished sketching the profile.
If the current viewport contains a two-dimensional or axisymmetric planar part, the part returns to its original orientation, and Abaqus/CAE cuts the plane with the sketched profile.
If the current viewport contains a three-dimensional part, Abaqus/CAE displays the part in its original orientation showing the base part, your sketched profile, and an arrow indicating the extrusion direction. The Edit Cut dialog box appears. Complete the following steps to create the extruded cut in the three-dimensional part:
- Click
 in the Edit Cut dialog box to reverse the extrusion direction, if necessary.
in the Edit Cut dialog box to reverse the extrusion direction, if necessary.If the arrow direction is difficult to see, use the rotate tool to rotate the part.
- Select one of the following end conditions:
-
Select and enter a value in the Depth field to specify the distance through which Abaqus/CAE will extrude the sketched cut profile.
-
Select to specify that Abaqus/CAE will extrude the cut up to a selected face.
-
Select Through All to specify that Abaqus/CAE will extrude the cut from the sketch plane completely through the geometry.
If desired, choose one of the following:
-
Select Twist and enter the pitch. The pitch is the extrusion distance in which a 360° twist would occur. The sketched cut profile must include an isolated point that indicates the center of twist.
-
Select Draft and enter the draft angle (greater than −90° and less than 90°). A positive draft angle indicates that external faces of the profile expand and internal faces contract.
Click OK to extrude the profile.
If you selected the twist option and your sketch includes a single isolated point, Abaqus/CAE uses that point as the center of twist. If your sketch does not include an isolated point, Abaqus/CAE returns to the Sketcher for you to create one. If your sketch contains more than one isolated point, Abaqus/CAE returns to the Sketcher and prompts you to select an isolated point as the center of twist.
If you selected , Abaqus/CAE prompts you to select the face to which to extrude the profile. Select a face to meet the following requirements:
-
the selected face does not have to be parallel to the sketch plane,
-
it can be a nonplanar face,
-
it must completely contain the extruded selection, and
-
it cannot be a datum plane or orphan element face.
Abaqus/CAE creates the extruded cut feature.
Note:
Cut features are applied to part geometry only. Any orphan elements within the cut region are unaffected by the cut.

 tool, located with the cut tools in the
tool, located with the cut tools in the  to return to the original view.
to return to the original view. in the
in the