Context:
If you select a curved edge or if you select two points connected by a curved edge, the corresponding edge of the resulting N-sided patch follows the contour of the edge. However, if you select points that are not connected by an edge, the patch simply connects the points; the patch will not follow the contour of the cell, and the partition may be incomplete.
From the main menu bar, select .
The Create Partition dialog box appears. Abaqus/CAE displays prompts in the prompt area to guide you through the procedure.
From the Type radio buttons at the top of the dialog box, choose Cell.
The Method list displays the methods that you can use to partition a cell.
From the list of methods, select N-sided patch.
If the part or assembly contains more than one cell, select the cell to partition.
Abaqus/CAE highlights the selected cell.
From the buttons in the prompt area, select the method to define the N-sided patch:
-
Use the Select Edges method to partition a cell by defining an N-sided patch from a sequence of selected edges. Use the text field in the prompt area to select the method of choosing edges:
- Loop
Select a single edge, and allow Abaqus/CAE to search for a continuous loop of connected edges that will partition the cell, as shown in the following figure:
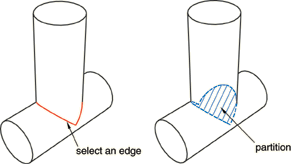
The edge that you select must be on the boundary of the cell being partitioned, and Abaqus/CAE must be able to form a closed loop from a series of connected edges. The resulting patch can have any number of edges. Abaqus/CAE highlights the loop that will form the patch.
- Edges
Manually select the edges that will partition the cell. The edges that you select must be on the boundary of the cell being partitioned. You can select any number of edges, and the selected edges must form a closed loop.
-
Use the Select Corner Points method to partition a cell by defining an N-sided patch using three to five selected points. Abaqus/CAE creates the patch by connecting the points in the order that you select them; consequently, the order in which you select the points is significant. The points can be vertices, midpoints, or datum points and must be on the boundary edges of the cell being partitioned. If a curved edge connects two of the points, the patch follows the contour of the curve, as shown in the following figure:
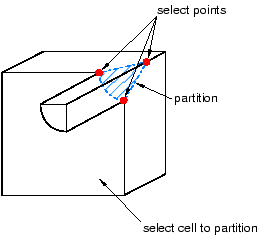
Abaqus/CAE highlights the selected points along with the edges that will form the patch.
Do one of the following:
-
If the highlighted edges indicate that Abaqus/CAE will create the desired partition, click Create Partition in the prompt area.
Abaqus/CAE creates the partition.
-
To change the selection of edges, click the Previous button ( ) to undo the previous step.
) to undo the previous step.
 tool, located with the partition cell tools in the module toolbox. For a diagram of the partition tools in the toolbox, see
tool, located with the partition cell tools in the module toolbox. For a diagram of the partition tools in the toolbox, see  ) to undo the steps in a procedure.
) to undo the steps in a procedure.
