General Information | ||||
|
| |||
In the following figure an example of non-parametric shape optimization is demonstrated. (Pictures by courtesy of Audi AG).
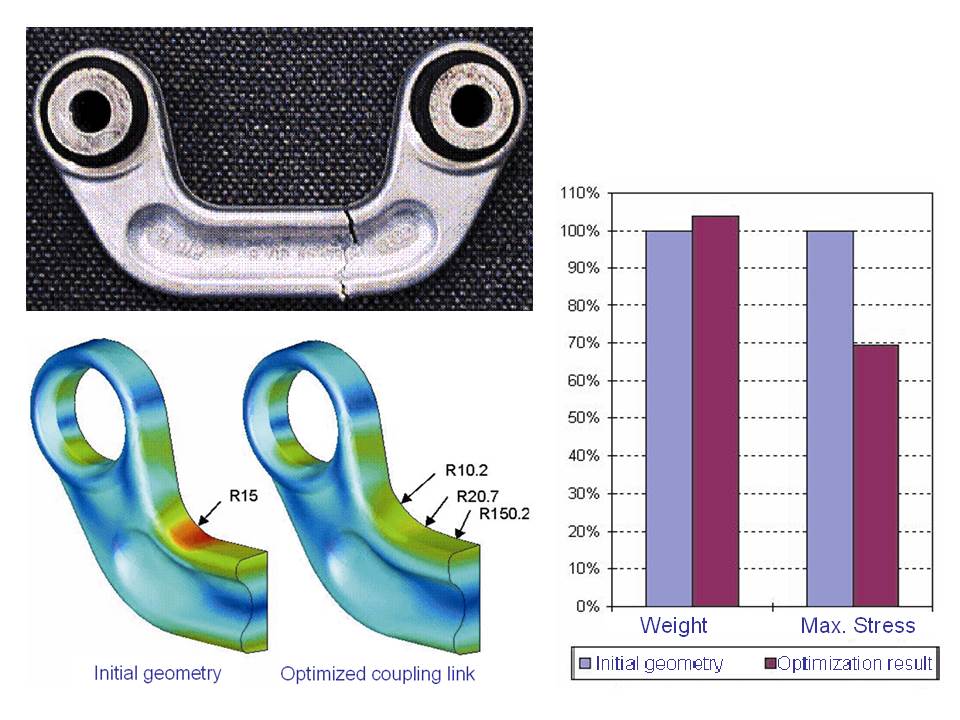 |
Typically, the objective function is to minimize stress concentrations. Based on the results of a stress analysis modifications of the surface geometry of a component are performed until the required stress level is reached. This process is usually carried out manually by trial-and-error.
SIMULIA Tosca Structure.shape allows an automatization of this improvement process. The surface geometry of a given FE model is modified iteratively based on the FE results, such that the required optimization target is reached. The start model is taken from an existing design, which should be improved, or from a previous topology optimization.
SIMULIA Tosca Structure.shape enables you to perform the following tasks
- Minimization of the equivalent stress
- Maximization of selected natural frequencies
Under the possible restrictions:
- Specification of a volume constraint
- Surface-based manufacturing constraints for casting, forging, stamping, extrusion and drilling
- Minimum and maximum member size
- Symmetry constraints
- Specification of design domain restrictions by FE meshes
- Mesh adjustment and mesh smoothing in each optimization cycle
Additional functionalities like optimization using durability results are available with SIMULIA Tosca Structure.durability. Functionalities like optimization using nonlinear results or optimization of contact areas are available with SIMULIA Tosca Structure.nonlinear.
Sensitivity-based shape optimization
Sensitivity-based shape optimization (SHAPE_SENSITIVITY) makes it possible to define very complex optimization tasks. It has been shown in industrial size examples that the method is very powerful and attractive for problems with many CONSTRAINTs.
The typical problems which can be solved by this algorithm are:
- Minimize volume with stiffness or displacement constraint
- Minimize volume with stress constraint
- Maximize stiffness (linear static) with a volume constraint
- Minimize displacement for critical nodes (linear static) with a volume constraint
- Maximize first eigenvalue (modal) with a volume constraint
- Maximize a certain eigenvalue (using mode tracking)
- Move eigenvalues away from certain frequency (band gap optimization with modal analysis)
| Important:
|
- Analysis types
-
Analysis type Supported Linear Analysis Yes Linear modal (no pre-tension) Yes Frequency response Yes Non-linear contact only, linear material, linear strains (NLGEOM=NO) Yes Non-linear material (e.g. *PLASTICITY) No Non-linear strains (NLGEOM=YES) No - Other boundary conditions
-
- Prescribed displacements are also supported.
- Temperature pre-loading is NOT allowed.
- Forces, surface forces, gravity forces and contact forces on design nodes are NOT supported as well.