Guidelines for Optimization of Structures with Non-Linear Behavior | ||
| ||
Volume/Mass Constraint in the Model
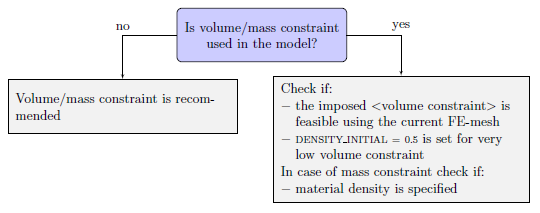 |
In cases where volume/mass constraints are in the model, it is important to check if the corresponding constraint values are feasible with respect to the given FE-mesh size. For example if we consider a square plate which is discretized by 9 square elements and use a relative volume constraint of 1/9, then we can not expect a black and white solution where some corners of the structure are connected. Set the DENSITY_INITIAL = 0.5 in cases where very low volume constraints (for example 0.05) are used to stabilize the optimization. If the volume constraint is not satisfied or there are unconnected regions in the resulting optimized structure, follow the given guidelines. Finer meshing of the structure i.e increasing the number of elements appropriate for the volume constraint can overcome these problems.
![]()
Minimize Volume/Mass as Objective
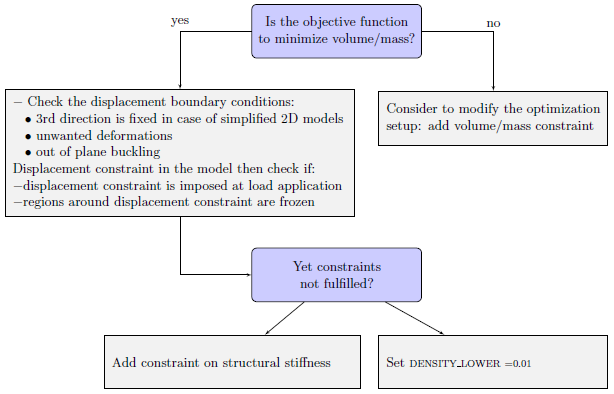 |
In cases where volume/mass is used as objective function follow the recommended procedure in order to avoid convergence issues. Check the displacements boundary conditions with respect to 3rd direction if 3D models are used to simulate 2D structures. Also check for unwanted deformations and out of plane buckling. In cases where displacement constraints are involved in the model, define these constraints at load application and freeze regions around displacement constraints. If the above setup does not help to satisfy the constraints, then impose additional constraints on the structural stiffness to stabilize the optimization. This is necessary in order to avoid structures acting like compliant mechanisms. If solver convergence issues appear during optimization procedure, set DENSITY_LOWER = 0.01. This can help to reach convergence, but it aids in creation of mechanism designs (because it increases unphysical stiffness of holes) which are not favored in most cases.
![]()
Topology Optimization in Context of Non-Linear Structural Analysis
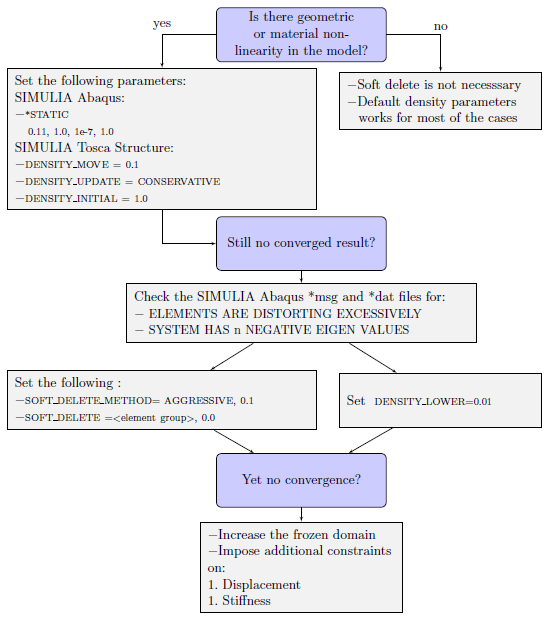 |
The above setup is considered to be stable for running topology optimization of structures with non-linear behavior. Even though the settings consume more time for convergence, the optimization may converge in the first attempt. The recommended settings are: small initial time increment, DENSITY_MOVE = 0.1, DENSITY_UPDATE = CONSERVATIVE, DENSITY_INITIAL = 1.0. If there are still convergence issues on solver side, check in case of SIMULIA Abaqus for the above mentioned warnings in the *.msg and *.dat files. If those warnings are found activate the soft delete procedure by adding SOFT_DELETE_METHOD = AGGRESSIVE, 0.1, SOFT_DELETE = <element group>, 0.0 This option offers the possibility of removing soft elements which could be distorted during the optimization process. Another alternative would be to change DENSITY_LOWER=0.01. One of the trivial methods of stabilizing a non-linear optimization task is by increasing the frozen domain. If convergence issues retain, impose additional constraints on displacement or structural stiffness to further stabilize the optimization procedure.
![]()
Manufacturing Constraints in the Model
In cases where manufacturing restrictions are used in the model:
- It is crucial to set the correct origin of the co-ordinate system and the axis corresponding to the restrictions in the parameter file.
- In case of non-linear problems, if the optimization ends in the solver convergence issues it is recommended to remove the manufacturing constraints and solve the convergence issues. After obtaining converged result, impose the restrictions one after the other.
![]()
Thermal Expansion in the Model
For thermal expansion problems, it is recommended to use the ENERGY_STIFF_MEASURE design response instead of STRAIN_ENERGY desing response.
![]()
Contact in the Model
For highly non-linear contact problems, automatic stabilization technique offered by the solver SIMULIA Abaqus is recommended. This option helps automatically control rigid body motion before the contact closure restrain such motion which can be activated by *CONTACT CONTROLS, STABILIZE command.
By default auto-frozen option is activated in SIMULIA Tosca Structure which affects regions with contact, load and displacement boundary conditions. Hence it is important to deactivate the Auto frozen option AUTO_FROZEN=OFF to acquire the contact regions as design domain in cases where it is necessary. Note, this setting can lead to solver convergence issues.
![]()
Minimize Stress as Objective
In cases where stress design responses are utilized to define the objective function it is recommended to give reference values for the corresponding design responses.
If stress design responses are used in the model, it is recommended to use sensitivities calculated by the solver SIMULIA Abaqus.