About the Shaft Example | ||
| ||
About the Model
During restriction-free optimization a non-symmetrical stress distribution will create a non-rotational symmetrical structure. Using the functionality LINK_SHAPE symmetrical requests are guaranteed. A shaft that has been manufactured by turning is optimized in this example. The rotational symmetry must be maintained during optimization. The following figure represents the initial model with boundary conditions and the deformed structure.
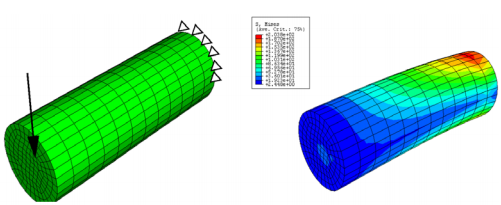
In order to maintain the rotational symmetry the nodes on the surface of the shaft must have the same z-coordinates as those in the global cylindrical coordinate system. These nodes must be selected as a group and link conditions are arranged that couples the absolute displacement. The command GROUP_AUTO_DEF is used in SIMULIA Tosca Structure to define the respective node groups. This command allows a simple, automatic definition of these node groups.
![]()
Procedure Summary
Note: For Tosca ANSA® environment:
This optimization task represents an advanced example. The optimization task definition using only the task manager in Tosca ANSA® environment is not possible. This makes the use of the Modules Buttons necessary.
| Model: | shaft.ext |
| Design Area: | Node group design_nodes |
| GROUP_AUTO_DEF: | Automatic definition of node group using the node group parent (contains all nodes in the length of the shaft) |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Left and right faces of the shaft (node groups left_nodes and right_nodes) are fixed in global z-axis direction |
| Design Variable Constraint: | Nodal displacements of all surface nodes on one diameter are the same in order to guarantee a turnable structure. |
| Mesh Smooth: | Mesh smoothing of all elements, while free surface nodes remain free |
| Objective: | Minimize the maximal von Mises stresses in the design area |
| Stop Condition | The global stop condition is set to 5 iterations |