Preprocessing, simulation, and postprocessing | ||
| ||
These three stages are linked together by files as shown below:
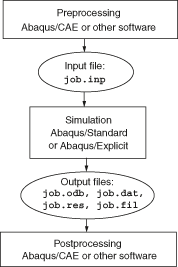
- Preprocessing (Abaqus/CAE)
-
In this stage you must define the model of the physical problem and create an Abaqus input file. The model is usually created graphically using Abaqus/CAE or another preprocessor, although the Abaqus input file for a simple analysis can be created directly using a text editor.
- Simulation (Abaqus/Standard or Abaqus/Explicit)
-
The simulation, which normally is run as a background process, is the stage in which Abaqus/Standard or Abaqus/Explicit solves the numerical problem defined in the model. Examples of output from a stress analysis include displacements and stresses that are stored in binary files ready for postprocessing. Depending on the complexity of the problem being analyzed and the power of the computer being used, it may take anywhere from seconds to days to complete an analysis run.
- Postprocessing (Abaqus/CAE)
-
You can evaluate the results once the simulation has been completed and the displacements, stresses, or other fundamental variables have been calculated. The evaluation is generally done interactively using the Visualization module of Abaqus/CAE or another postprocessor. The Visualization module, which reads the neutral binary output database file, has a variety of options for displaying the results, including color contour plots, animations, deformed shape plots, and X–Y plots.