How do mesh elements correspond to Abaqus elements? | ||
| ||
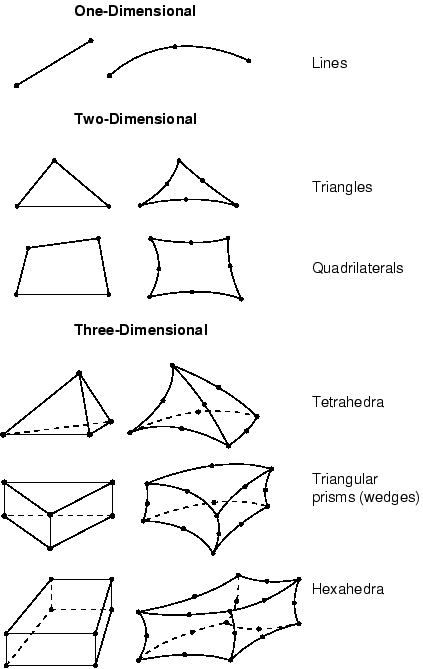
Most elements in Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit correspond to one of the shapes shown; that is, they are topologically equivalent to these shapes. For example, although the elements CPE4, CAX4R, and S4R are used for stress analysis, DC2D4 is used for heat transfer analysis, and AC2D4 is used for acoustic analysis, all five elements are topologically equivalent to a linear quadrilateral.
Every mesh region has one or more Abaqus element types assigned to it by default. Each element type corresponds to an element shape that can be used in the region. For example, a shell mesh region typically has a quadrilateral and a triangular element type assigned to it by default. However, you can change the element assignment for any Abaqus element that is topologically equivalent to the element shape assigned to the region. As a result, you can choose to mesh a shell region with only all triangular elements, and Abaqus/CAE ignores the quadrilateral element assignment.
To change the element assignment to an Abaqus element that is topologically equivalent to the element shape assigned to the region, select from the main menu bar. Similarly, you can select to select the element shape for meshing.
However, since no element type checking is done until you submit the analysis, it is possible to choose an element that is inappropriate for the analysis you will be conducting. For example, Abaqus/CAE does not prevent you from specifying heat transfer elements such as DC2D4, even though you may be conducting a stress analysis.